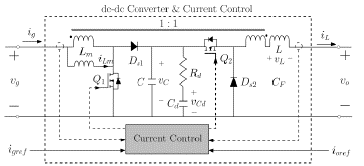
Electronics | Free Full-Text | Buck-Boost DC-DC Converters for Fuel Cell Applications in DC Microgrids—State-of-the-Art

A novel low-ripple interleaved buck–boost converter with high efficiency and low oscillation for fuel-cell applications - ScienceDirect

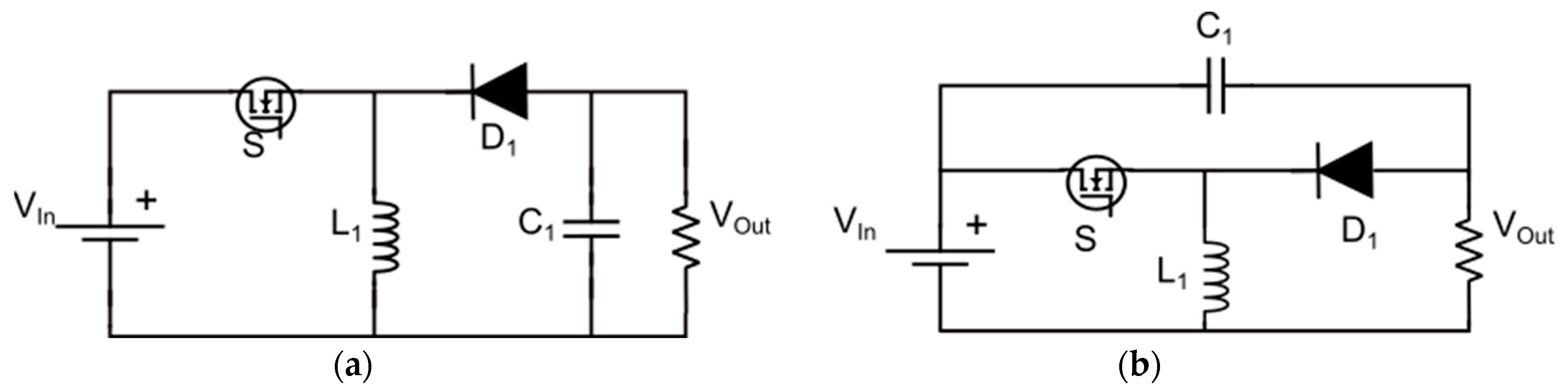
Processes | Free Full-Text | Non-Inverting Quadratic Buck–Boost Converter with Common Ground Configuration for Supercapacitor Applications

Analysis, control and design of a non-inverting buck-boost converter: A bump-less two-level T–S fuzzy PI control - ScienceDirect

PSO optimized PI controlled DC‐DC buck converter‐based proton‐exchange membrane fuel cell emulator for testing of MPPT algorithm and battery charger controller - Premkumar - 2021 - International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems -

A two‐phase non‐inverting buck‐boost converter for an RL load - Liao - 2022 - The Journal of Engineering - Wiley Online Library

Analysis, control and design of a non-inverting buck-boost converter: A bump-less two-level T–S fuzzy PI control
Pre-calculated duty cycle optimization method based on genetic algorithm implemented in DSP for a non-inverting buck-boost converter | SpringerLink
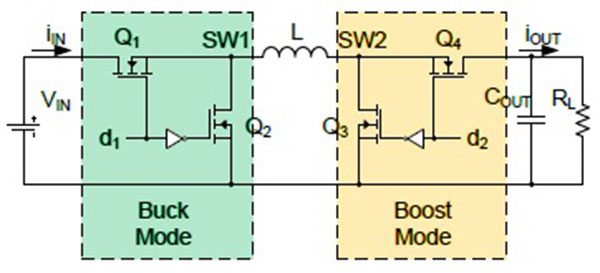
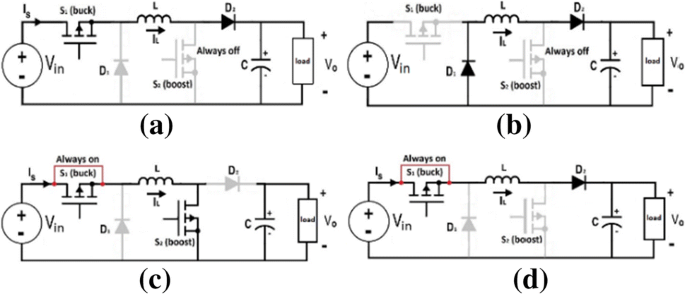
Modeling and Controlling Strategy of Four-Switch Buck-boost Convertor with Smooth Mode Transitions ~ Fulltext

A Novel Low Current Ripple Magnetically Coupled Interleaved DC-DC Buck-Boost Converter with High Efficiency and Continuous Transfer-Function for Fuel-Cell Applications
Comparative analysis of non-inverting buck-boost converter topologies for fuel cell low voltage applications

a) Topology of H-bridge for the buck–boost converter and (b) energy-... | Download Scientific Diagram
Fuzzy/State-Feedback Control of a Non-Inverting Buck-Boost Converter for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles
A High Efficiency Non-Inverting Multi Device Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter with Reduced Ripple Current and Wide Bandwidth for Fuel